


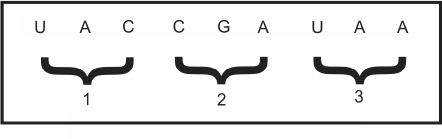
GCC --- AUA --- GGA (in sequence)
Glycine --- Proline --- Serine (in sequence).

3
ATG.
It determines the codes for the sequence of amino acids which determines the type of protein
AUG
tRNA picks up specific amino acids
its anticodon matches up with the codon of mRNA
therefore the amino acids are arranged in a particular sequence
to form particular polypeptides/proteins
M - DNA
R - Ribosome
AGT
Transcription

Threonine
CCG
Anticodon
A different protein may form because it has cysteine instead of serine / have different amino acids.

A: Nuclear membrane
B: mRNA
D: DNA
Carrying hereditary characteristics from parents to their offspring.
Controls the synthesis (manufacturing) of proteins/controls the structure and functioning of cells.
Transcription
Enzymes
Ribosome
Translation
The mRNA strand from the nucleus becomes attached to a ribosome with its codons exposed
each tRNA molecule carrying a specific amino acid according to its anticodon
matches up with/complements the codon of the mRNA
so that the amino acids are placed in the correct sequence
adjacent amino acids are linked to form a protein


