




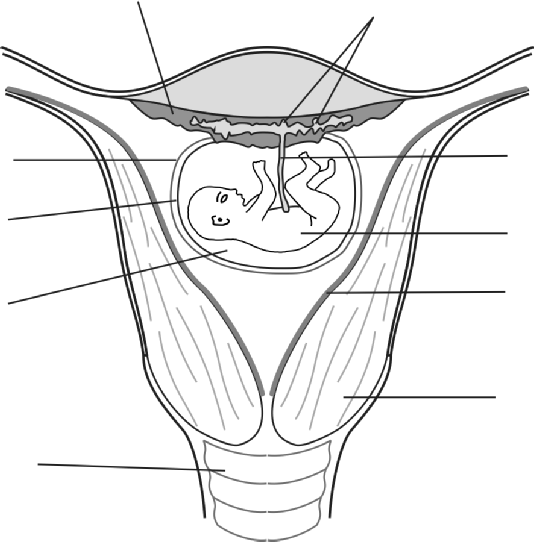










1. Forms link between mother and foetus.
2. Serves as organ for gaseous exchange, excretion and nutrient supply for the foetus.
3. Serves as a micro-filter by preventing bacteria entering the foetus.
4. Produces antibodies to provide passive immunity for the foetus.
5. Secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine wall whilst pregnancy lasts.

A: Umbilical cord
B: Placenta
Has folds/villi to enlarge the surface area.
Enriched with blood vessels for transport of gases/ nutrients/ waste products.
Selective permeable membranes to promote diffusion of gases/ substances.
Contains blood sinuses to bring blood of mother in close association with that of foetus.
(Any 1)
Acts as a shock absorber/prevents mechanical damage.
Prevent great variation in temperature.
Allows for movement of the foetus.
Passes out before birth to lubricate the birth canal.
(Any 2)
Foetal alcohol syndrome
Woman given fertility drugs to produce many eggs at the same time.
Eggs collected and placed in a petri dish with a special solution.
Sperm collected from male are allowed to mix with the eggs in the petri dish.
Fertilised egg divides repeatedly to form the blastula. The blastula is placed into the woman’s uterus.
Normal development of the foetus occurs.

